The business aviation market in 2025 is entering a new era, driven by the rise of jet-sharing, the development of more sustainable private jets and increasing regulatory pressure in Europe. Between environmental taxation, artificial intelligence and ultra-personalized services, private jet operators must adapt their models to meet rapidly changing demand. AEROAFFAIRES, the private jet rental specialist, deciphers the 2025 trends that are reshaping the future of business aviation.
Bilan 2024: figures and dynamics of the private aviation market
According to Global Market Insights, North America dominated the business jet market in 2024, accounting for 63.5% of market share. In the United States, private aviation is growing rapidly, driven by increased demand for long-haul flights, luxury customization options and on-demand rental services.
Projections by The Business Research Company indicate that the global market for private jet rental services will grow from $21.24 billion in 2024 to $24.28 billion in 2025, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.3%. This growth is attributed to increased demand for flexible, customized travel solutions, as well as an increase in the number of affluent individuals and business travelers seeking alternatives to commercial flights.
- Fractional ownership and jet sharing are gaining ground, making private aviation more accessible and flexible. These models help reduce costs while enjoying the exclusive benefits of private jet travel.
- The year 2024 marks a phase of transformation for business aviation, notably due to the consolidation of major players and the rise of sustainable initiatives.
- Advances in service digitization, flight management and carbon tracking have become key differentiators.
In 2025, business aviation will continue its transition towards greater efficiency, flexibility and sustainability, confirming its central role in the mobility of companies and major international decision-makers.

Demand trends for 2024-2025
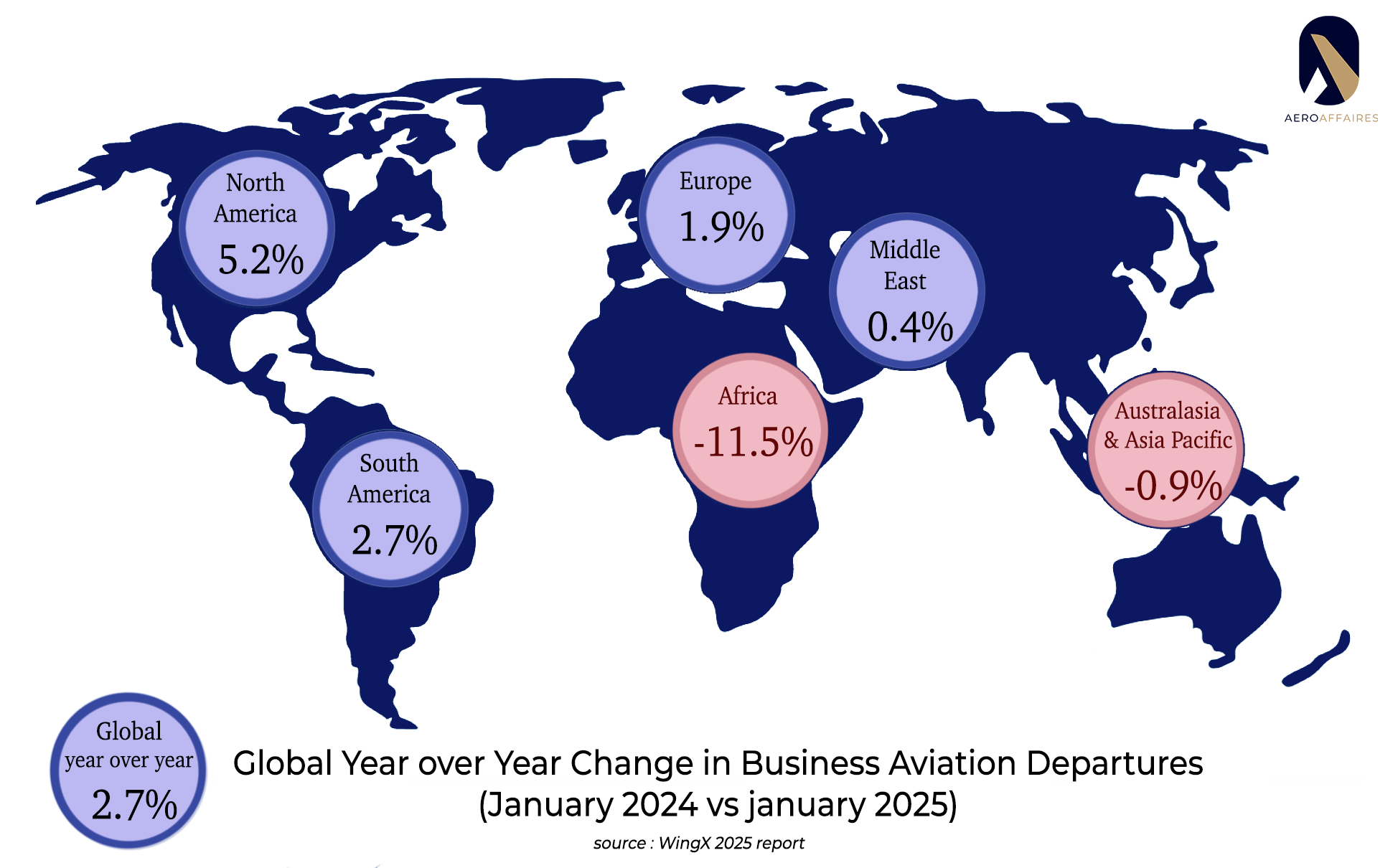
In 2025, global demand for business aviation grew by +3.8% year-on-year.North America was the market’s driving force, with a 5.2% increase, driven by the strong performance of super-light jets (+19.4% YOY*).Europe saw a more measured rise (+1.9%), with markets such as Belgium (+10.6%) and France (+6%) outperforming the regional average.
By contrast, Africa declined sharply (-11.5%), penalized by a 14.4% drop in intra-regional flights, despite a strong recovery in Kenya (+63% YOY).Latin America grew by 2.7%, led by Brazil (+13.5%). Finally, Asia-Pacific remained virtually stable (-0.9%), with a few pockets of growth, notably in the Philippines (+38% YOY).*year over year .
Technological innovations and upmarket private jets
Technological innovation and sustainability in business aviation
The private aviation industry is at the forefront of many technological innovations. Manufacturers and operators are investing heavily in the development of more efficient, quieter and more environmentally-friendly aircraft. This trend is driven by a dual requirement: to reduce operating costs and to improve the sector’s ecological footprint.
Notable advances include :
- New-generation engines, offering lower fuel consumption
- Increased use of composite materials, lightening aircraft structures
- The development of sustainable aviation fuels (SAF)
- Integration of advanced avionics systems for more precise and economical navigation

Sustainability is becoming a major selling point in business aviation. Customers, increasingly sensitive to environmental issues, are demanding greener travel solutions. This trend is driving the industry to accelerate research into green technologies, including the electrification of short-haul aircraft.
The following table illustrates the comparison between conventional jets and the new eco-efficient models:
| Criteria | Conventional jet | Eco-efficient jet |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel consumption | High | Reduced by 20-30 |
| Significant CO2 | emissions | Reduced by 25-35 |
| Noise level | High | 50% reduction |
| Operating costs | Standard | 15-25% lower |
Ultrapersonalization, a strategic pillar of private aviation
In private aviation, personalized attention to detail is a key differentiating factor in meeting the expectations of the most demanding customers. Far beyond the simple flight, operators today offer a 360-degree tailor-made service, including the selection of aircraft adapted to the passenger’s preferences, customizable interiors and a complete concierge service. From the booking of private transfers to the organization of exclusive stays, everything is anticipated to offer a seamless travel experience, combining comfort, confidentiality and flexibility. This global approach positions business aviation as a true art of living, serving the mobility of decision-makers and international elites.
AI, combining efficiency and attention to detail
This ultrapersonalization is further enhanced by the rise ofartificial intelligence, which is gradually revolutionizing the private aviation sector, optimizing every stage of the customer experience and operational management. Thanks to AI, operators can optimize aircraft allocation and adapt routes in real time to reduce costs and emissions. On the passenger side, AI makes it possible to offer a hyper-personalized travel experience, with tailor-made recommendations, anticipation of culinary or entertainment preferences, and even destination suggestions based on the customer’s profile. A real competitive lever, artificial intelligence is a strategic asset for combining efficiency, responsiveness and service excellence in business aviation.
The rise of jet-sharing and on-demand flight services
One of the most striking trends in the private aviation market is the emergence of jet-sharing and on-demand flight services. Jet-sharing has developed in particular to meet the transportation needs of major events,when many customers travel to the same place at the same time. The sharing of private jets makes it possible to offer fares per seat, making private jet travel more affordable.
For example, duringmajor sporting events such as the Super Bowl, there is a significant increase in the number of private flights. Travelers choose to share costs and optimize aircraft availability to attend these events. Similarly, cultural festivals or business conferences attract large numbers of participants who turn to jet sharing to benefit from the flexibility and comfort of private jets, while enjoying optimized costs thanks to the division of expenses between several passengers.
This growth comes against a backdrop in which super-light jets, often used for these shared services, recorded a significant increase of +19.4% YOY over the same period.
Online booking platforms also play a vital role in this democratization. They match passengers with a fleet of available private aircraft, similarly optimizing aircraft utilization and reducing costs for customers. In addition, growing awareness of environmental issues is prompting travelers to consider jet-sharing as a more sustainable option, optimizing the use of resources and reducing the carbon footprint per passenger.
These services are attracting a new clientele, looking for an alternative to the constraints of commercial flights without having to invest in a personal jet. This relative democratization of private aviation is stimulating market growth and prompting traditional players to review their offerings.

Increased taxation and environmental regulations within the EU
Context
Business aviation in Europe is undergoing a major transformation as a result of new environmental and fiscal regulations. Indeed, the European Union has committed itself to a massive decarbonization of air transport as part of the Green Deal and the “Fit for 55“ legislative package. This program calls for a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, with a particular focus on air transport, considered difficult to decarbonize.
Key measures include increased kerosene taxation, mandatory sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) quotas, a strengthening of the carbon market (EU ETS), as well as national regulations in certain countries. These developments have a direct impact on the operating costs of private jets, and could redefine the sector’s business models.
End of tax exemption on kerosene: a gradual rise in costs
Historically exempt from fuel taxes, kerosene used by private aviation is now subject to increasing taxation under the impetus of the European Union. The “Fit for 55” package introduces a harmonized fuel tax for intra-European flights, with a gradual increase from 2025. By 2030, the cost of kerosene could rise from €0.33 to €0.50 per liter, representing an additional cost of around €200 to €300 for a Paris-Nice flight on a Cessna Citation CJ4 consuming 600 liters.
Mandatory SAF quota: a transition to greener fuels
The European Union is also imposing the gradual incorporation of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) in the fuel tanks of private jets. From 2025, a minimum of 2% SAF will be mandatory, rising gradually to 70% by 2050. Although this measure aims to reduce the carbon footprint of business aviation, it will also drive up costs, as SAF is currently 3 to 5 times more expensive than conventional kerosene.
Cumbersome carbon market (EU ETS): increasing pressure on operators
Intra-European business flights are subject to the European Union Emissions Trading Scheme (EU ETS), requiring operators to purchase credits to offset their CO2 emissions. In 2024, the price of a carbon allowance will fluctuate between €70 and €100 per tonne of CO2. As an example, a Cessna Citation Mustang making a flight from Paris to Geneva emits an average of 1.5 to 2 tonnes of CO2, representing an estimated additional cost of between €150 and €200 per journey.
The European Union is considering strengthening the ETS market by reducing free allowances and aligning it with the international CORSIA system. By 2030, the price per tonne of CO2 could reach €150, further increasing the cost of private jet travel.
At national level
At the same time, several countries continue to adopt national tax measures to increase the burden on private jets:
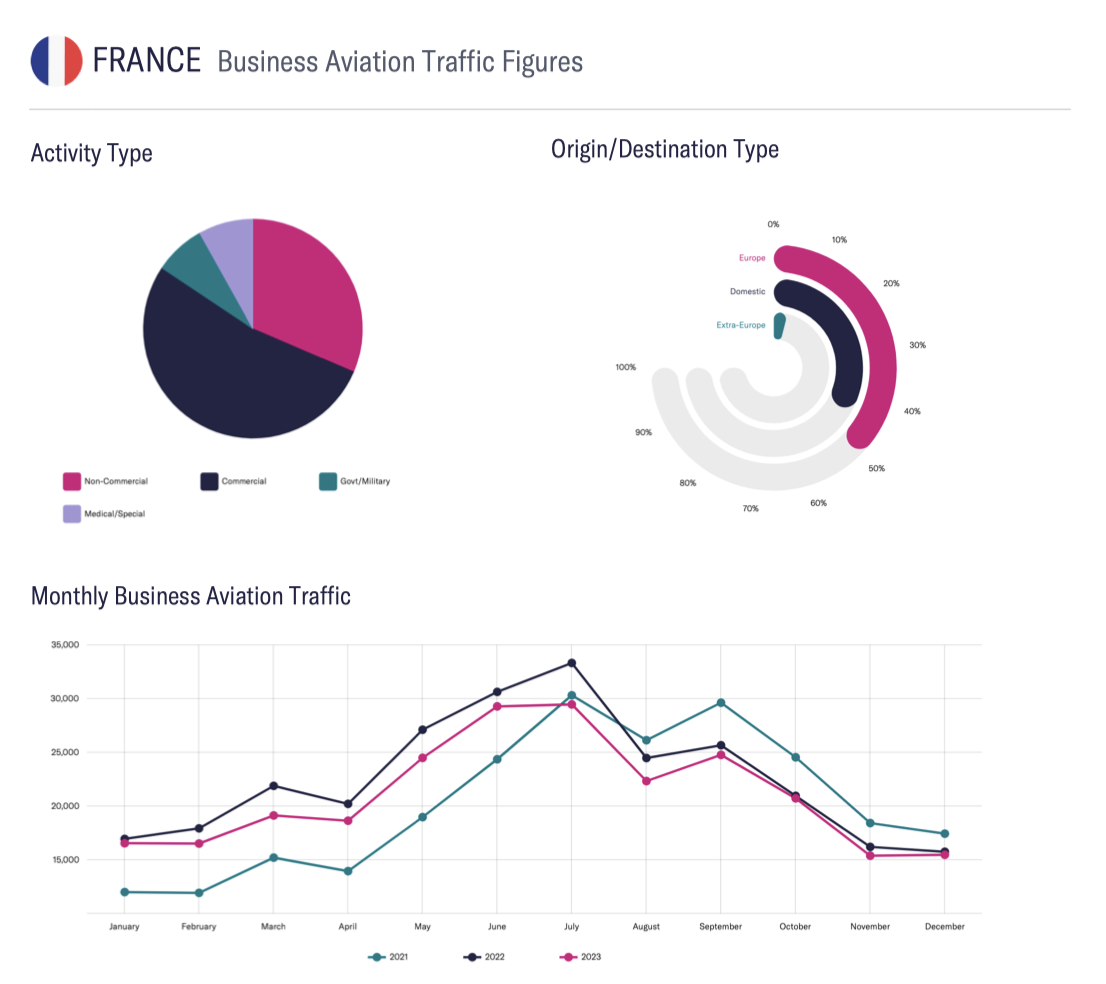
- France: The TSBA tax (Taxe de Solidarité sur les Billets d’Avion) has risen sharply as of March 1, 2025 in the private aviation sector, by up to €2,100 per passenger, per trip on long-haul flights.
- Belgium: In 2023, a new environmental tax was introduced on private flights departing from Belgian airports. The tax is calculated according to the distance flown and the aircraft’s noise level. For example, a flight from Brussels to Nice in a Falcon 900 generates a tax of around €600.
- Netherlands: Since July 2021, private jets have been subject to an environmental tax. Each passenger must pay an amount of up to €525, compared with around €26 for a passenger on a medium-haul commercial flight.
What impact will this have on business aviation in Europe?
These new regulations aim to make private aviation more environmentally friendly, but they pose a major economic challenge for operators and customers alike, even if it means redrawing the take-off and landing map. Higher kerosene taxes, the gradual adoption of FAS and the growing importance of the carbon market will lead to a significant increase in private flight fares in Europe.
Against this backdrop, jet sharing and fractional co-ownership will see their growth accelerate even further to optimize costs while reducing environmental impact. In addition, technological innovation in engines and aerodynamics will play a key role in adapting the sector to this new era of sustainable aviation.
Social watch
Pressure is not only coming from regulators. Public and media perception of business aviation has deteriorated sharply, driven by campaigns denouncing its disproportionate carbon footprint. Private aviation, often perceived as a symbol of ostentatious luxury, is particularly scrutinized. This stigma is prompting some governments to consider tighter restrictions:
- Bans on short flights: Some countries are considering banning private flights of less than 500km, where a rail alternative exists.
- Slot restrictions: to reduce airport saturation and give priority to commercial and cargo flights, private jets are often the first to be targeted by regulations on the time slots reserved for take-off and landing. These are particularly rare and precious during major events (Salon du Bourget, Monaco Grand Prix, etc.), where demand is exploding.
- Flow monitoring: Initiatives are emerging to impose public traceability of business flights, to encourage self-regulation through societal pressure.
Operators will have to redouble their efforts to improve their carbon footprint and justify their social utility.
Evolving business models and market consolidation
The competitive landscape of private aviation is undergoing a profound transformation. Traditional players in the sector are facing the arrival of new entrants. This heightened competition is stimulating innovation and driving market consolidation.
There is a growing trend towards mergers and acquisitions, enabling companies to pool resources, broaden their offering and achieve critical mass. This consolidation aims to create economies of scale and improve profitability in a sector where margins can be tight.
At the same time, new business models are emerging, blurring the traditional boundaries between ownership, rental and on-demand services. Subscription programs are gaining in popularity, offering regular customers privileged access to a fleet of aircraft without the constraints of ownership. These hybrid formulas meet business travellers’ demand for greater flexibility.
Vertical integration is also becoming a popular strategy. Some operators are investing in their own maintenance or pilot training centers, with the aim of controlling the entire value chain and optimizing their costs. This approach also ensures a consistent, high-quality level of service, which is crucial in a premium market.
Future prospects and challenges
The future of the private aviation market looks both promising and complex. Global demand should continue to grow, driven by the increasing number of Ultra High Net Worth Individuals (UHNWIs) worldwide, particularly in emerging economies.
Theintegration of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and automation, represents both an opportunity and a challenge. These innovations promise to improve safety and operational efficiency, but require substantial investment and the adaptation of skills.
Finally, global economic volatility and geopolitical tensions can influence demand for private flights, making it crucial for industry players to diversify their markets and offerings.
Current trends reflect an industry in the throes of change, seeking to reconcile exclusivity, accessibility and environmental responsibility. Players able to innovate and adapt quickly to these new realities will be best positioned to thrive in this changing landscape.

Aeroaffaires at your service for your private trips
As a specialist in private jet charter, AEROAFFAIRES guarantees you a tailor-made, secure and competitive service. Your dedicated flight consultant is available 24/7 to organize your flight according to your requirements, up to 2 hours before departure.
Over 95,000 passengers have already placed their trust in us, on board more than 20,000 private aircraft. When you fly with AEROAFFAIRES, you also support our Sky CO2 program, dedicated to preserving ecosystems in France.
Get your quote online now or contact us on +33 (0) 1 44 09 91 82 or by email: charter@aeroaffaires.com.





