In France and in Europe, when you see an aeroplane in the sky, it is either a flight subject to public transport regulations or private transport. What impact do these differences have on your private jet flight?
According to article L330-1 of the Civil Aviation Code, public transport (TP) or public passenger transport (TPP) is that used to market aircraft flights to passengers. It is therefore the flights for which passengers pay and companies make a profit. Whether freight or passengers, the aircraft must be certified as public transport to market flights. This legal regime ensures greater security for passengers.

The Civil Aviation Code does not explicitly define private transport. It is specified that the two notions of transport are opposed. It is forbidden to ask for financial compensation for a private transport flight, the air travel service must be offered free of charge or only share the costs related to this flight.
As an air broker, AEROAFFAIRES only offers flights with air operators and flights under the public passenger transport regime.
In this article, our air experts explain the distinction between public and private transport.
Public transport certification, guaranteed security

Public transport certification is granted to aircraft of public or legal entities with an ATC (Air Transport Certificate).
An Air Operator’s Certificate (AOC) is an approval issued to an air operator allowing it to carry out commercial passenger transport operations for remuneration. This document certifies the airline’s ability to guarantee flights under the best safety conditions.
The competent authority of the member country issues this licence, which is valid in Europe. In France, it is the Direction Générale de l’Aviation Civile (DGAC) which is in charge of awarding public transport licences. The DGAC regulates access to this certification.
Public transport flight, a controlled safety regulation
Business aviation is subject to the same safety procedures and standards as major airlines such as American Airlines or Air France.
Worldwide, two bodies are responsible for monitoring the safety of civil aviation. On the one hand, the Federal Aviation Administration (or FAA). On the other, the European Aviation Safety Agency (or EASA).
Medical checks on pilots
When you are a pilot, it is compulsory to take a medical test every year. After the age of 40, the test is half-yearly, i.e. twice a year. From the age of 65, the pilot can no longer practice his profession. During the medical examination, an aviation doctor checks your general state of health. Pilots also undergo a urine test, an electrocardiogram, a blood test, a lung function test, an audiogram, an ENT examination and an eye examination. If the doctor does not validate the criteria, he or she may temporarily or permanently revoke the pilot’s licence depending on the abnormality.
Strict maintenance of the equipment
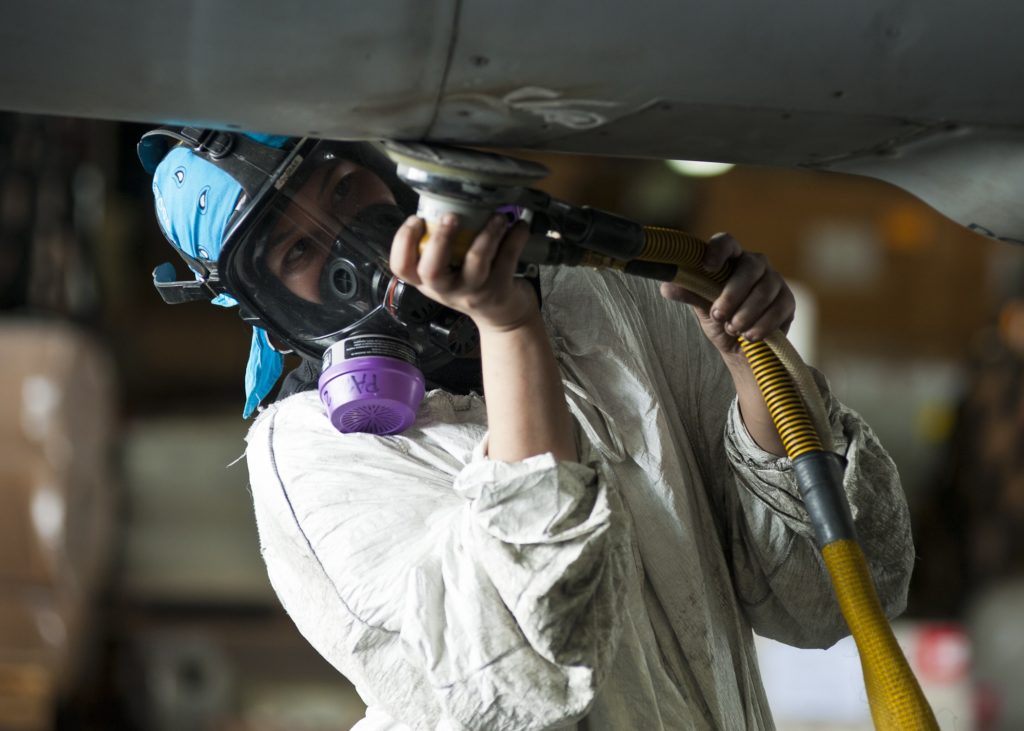
Private jets cannot be maintained in any structure. Aircraft must be maintained in a structure approved by its manufacturer and by the competent authority of its country of registration. In France, this is the DGAC. Depending on its use, there are 4 levels of maintenance ranging from A to D. Levels A and B correspond to an aircraft with no anomalies. These are maintenances carried out before and after each flight. Levels C and D are more extensive and bring the aircraft to a standstill for a longer period of time to check every detail of the aircraft. After a certain time, the technicians change the parts. This is done regardless of their condition.

Evaluating pilot knowledge
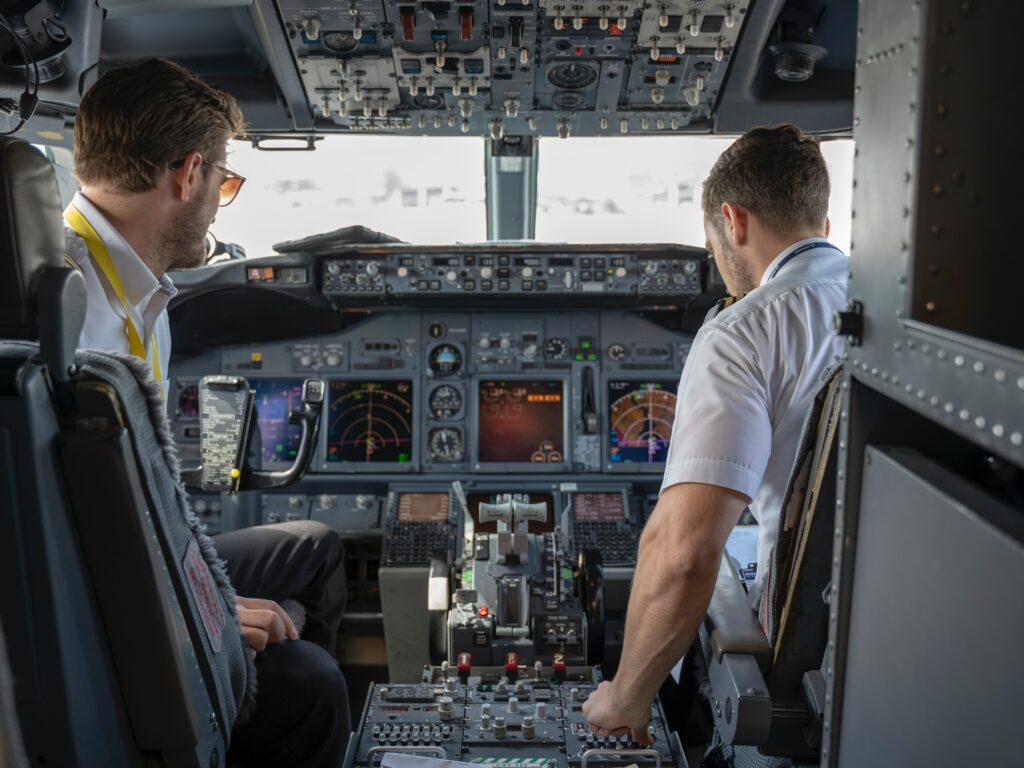
Once a year, pilots undergo technical knowledge tests on their environment in a simulator. These tests, supervised by instructors, aim to verify the pilot’s knowledge of his environment. The questions generally focus on the characteristics of specific aircraft, flight situations or specific airports.

Aircraft and passenger insurance
The airlines proposed by AEROAFFAIRES provide the flights. Depending on the range of the aircraft, the insurance policy covers amounts ranging from 10 to 500 Million USD. In order to offer the best guarantees to our customers, AEROAFFAIRES adds a cover of 20 Million Euros.

Enhanced aircraft performance for landings and take-offs
When an appliance leaves the factory, it has technical skills assigned by its manufacturer. These are obviously the result of numerous tests and flight hours.
On the other hand, the skills of certified public transport aircraft have evolved. Not because of technical modifications. But it is the EASA which has revised the official technical cutbacks in public transport. The aim of this approach is to guarantee a very high level of safety.

In this approach, the public transport certified aircraft that we propose have constraints concerning landings:
- Private jets must be able to stop on 60% of the length of an aerodrome’s runway.
- As for turboprops, they must be able to stop over 70% of the length of an aerodrome’s runway.
In the event of bad weather, or wet runways, these limits increase by 15% due to the runway’s loss of grip.
If aircraft are unable to land within this distance, they cannot access the aerodrome by public transport. With more room to manoeuvre, turboprops have access to more aerodromes.
For example, the runway at Saint-Tropez la Môle is only accessible to the Pilatus PC12 by public transport and to the Jet Mustang if weather conditions permit. While in owner’s flight, you could land a Falcon 7X or Phenom 300, the same goes for Courchevel or Gstaad airports which have very short runways.
Certification of private transport or owner flights, lighter supervision by the Civil Aviation Authority.
You receive the Private Transport Certification, once you pass the Private Pilot License (or PPL). With this licence it is possible to fly an aircraft.
Private transport certification has advantages and disadvantages. Private transport restricts the pilot’s activity, but also gives them more freedom.
Europe prohibits the marketing of a flight in private transport. When this is the case, it is called Illegal Public Transport. However, as private transport, you have the right to invite your family and friends on board.

It is possible to share the cost of the flight. When this is the case, it is called co-carriage. Platforms for putting people in touch with each other set up these practices between pilots, aircraft and passengers. However, these platforms do not have ATCs or public transport and are not liable in the event of an accident.
Flights under the private transport regime or private jets of owners have access to many more runways and aerodromes. However, you should first check the insurance contract to be sure of the cover offered. Because even if you have access to many runways, it is possible that not all of them are covered by your contract.
If you wish to hire an aircraft and its crew, you must ensure certain points for your safety. In particular, you must make sure that the structure to which the private jet belongs has an ATC. For example, that its aircraft are certified for public transport. You can see this on the flight plan number (Tail Number) sent by your broker: airlines submit a flight plan to civil aviation, mentioning the type of flight operated. On the flight plan, a letter specifies the type of flight:
G: General aviation (sport, business etc.)
S: Regular Air Transport
N: Non-Scheduled Air Transport
M: Military
X: Type of flight not corresponding to any of the above categories
If an unauthorised air operator operates a flight under the public transport regime, it is illegal passenger transport. In the event of an accident, passengers will not be covered for medical expenses or financial compensation. Indeed, insurers automatically stipulate a universal clause that allows them to be released from any financial responsibility in the event of an accident involving an “illicit” carrier.
Our aviation experts are available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week for your private flight on +33 (0) 1 44 09 91 82. Do not hesitate to go to our online quote to obtain a price estimate for your private flight.
Need a price estimate?
What distinguishes the quality of service in business aviation?
The quality of service in business aviation is characterised by high safety standards, increased flexibility in flight schedules, superior comfort compared to commercial airlines and personalised service for customers.
How are safety standards maintained in business aviation?
Safety standards are maintained in business aviation through regular aircraft inspections, professional and experienced flight crews, strict safety protocols and continuous training for crew members.
How does business aviation provide a personalised service for customers?
Business Aviation provides a personalised service for customers by allowing them to customise their travel experience, offering a concierge service for hotel and car reservations, providing private car transfers to the airport and offering a personalised luggage service. Crew members are also trained to provide attentive and personalised service to passengers.





